Do you and your family have adequate insurance cover?
Did you know there is a more tax-effective way to fund your insurance?
How does it work?
Personal insurance is a smart way to protect your quality of life and provide support for your loved ones if you get sick or injured.
While you often hear how important it is to have sufficient cover, it’s just as important to be smart about the structure of your insurance – so that the dollars you pay for premiums work harder for you.
Most types of life insurance can be held inside or outside of super. These include:
- Income Protection (IP). Pays a regular monthly benefit if you become severely disabled by sickness or injuries and you are unable to work – potentially helping your partner take time off work to care for you and/or cover mortgage repayments.
- Life cover. Pays a benefit if you die or become terminally ill – helping your family take care of debts and ongoing household expenses.
- Total & Permanent Disablement (TPD) cover. Pays a benefit if you are permanently disabled – helping cover the long-term costs of care for you and your family.
There are advantages and disadvantages to holding insurance inside or outside of super.
Advantages
Insurance inside super
- IP, Life and TPD (any occupation) insurance premiums are generally tax deductible to your super fund.
- You can pay your premiums using accumulated super money or by making additional super contributions – which may come from your before-tax income.
Insurance outside super
- IP insurance premiums are generally tax deductible.
- Life and TPD benefits are generally tax free*
- Insurance benefits are paid directly to you or your nominated beneficiary.
Disadvantages
Insurance inside super
- While most insurable events for IP, Term Life and TPD result in a condition of release, there are some limited situations where you may not be able to access the insurance benefits until you retire.
- The tax rate payable on a death benefit to non dependants may be up to 31.5%
Insurance outside super
- Term Life and TPD insurance premiums are generally not tax deductible when paid personally.
*Life insurance proceeds will be subject to CGT if paid to someone other than the original beneficial owner and that person / entity acquired the policy for consideration. TPD and is subject to CGT if the proceeds are paid to someone other than the life insured or a defined relative.
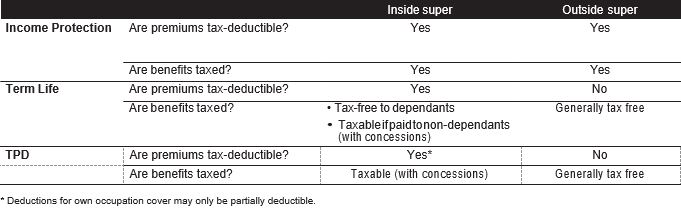
Tax treatment at a glance
The following table summarises the tax treatment of premiums and payouts (benefits) inside and outside super.
What does it mean for me?
Whether you have insurance cover inside or outside of super depends on your personal circumstances and needs. By choosing the right combination, not only can you have the appropriate insurance cover to give peace of mind, but you can do it in a cost and tax-effective manner.
Strategy in action
As the table below shows, the higher your marginal tax rate, the bigger the potential saving by taking insurance inside super. Before-tax cost of a $1,000 insurance premium:
| Taxable income | Marginal tax rate (inc. Medicare levy) | Before-tax cost outside super | Before-tax cost inside super |
| $37,001 – $80,000 | 34.5% | $1,527 | $1,000 |
| $80,001 – $180,000 | 39% | $1,639 | $1,000 |
| Over $180,000 * | 49% | $1,961 | $1,000 |
Source: BT Life Insurance. Assumes insurance is arranged through a taxed super fund.
Note: Most insurance premiums are tax deductible to your super fund so it may offset other taxable income (such as investment income and concessional super contributions) your fund receives throughout the year.
* The before tax cost will be higher for taxpayers with income greater than $300,000 due to additional tax payable on their concessional contributions. However the strategy of taking insurance inside super is still tax effective